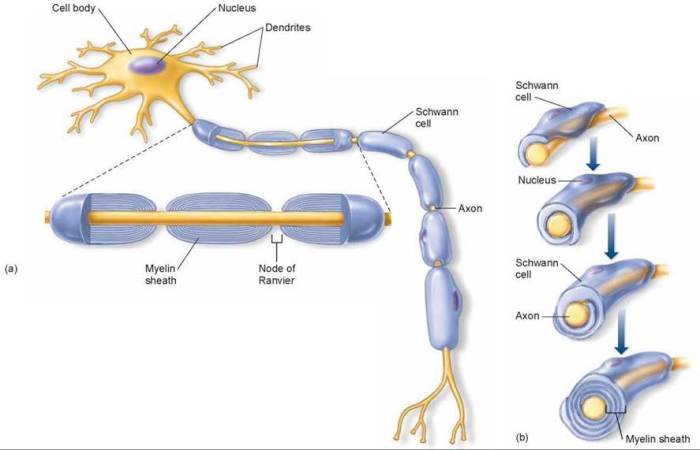
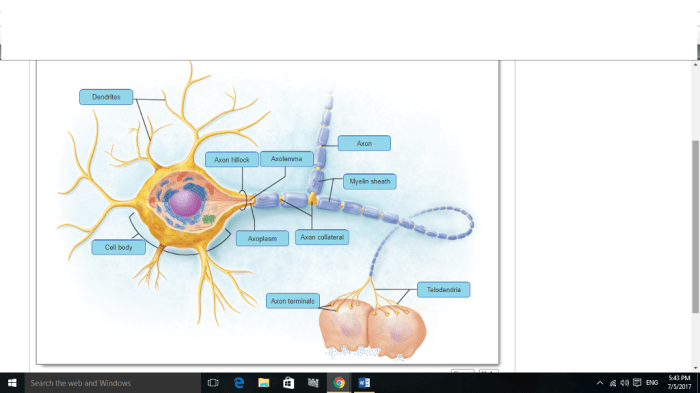
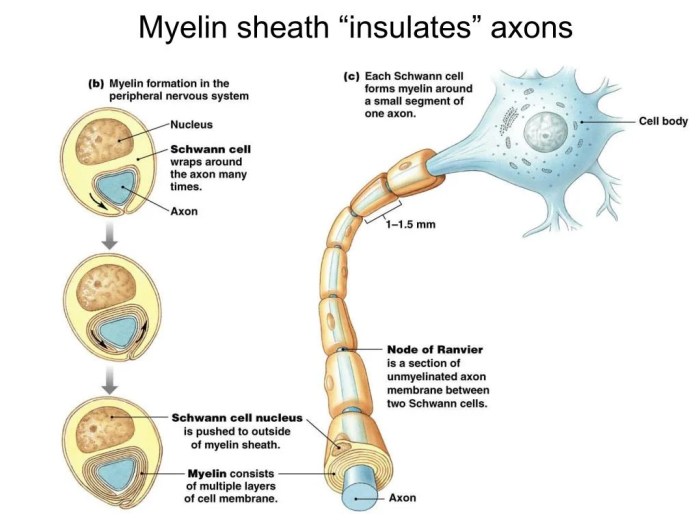
Art-labeling activity the myelin sheath in the pns and cns – In the realm of neuroscience, the art-labeling activity of the myelin sheath in the peripheral nervous system (PNS) and central nervous system (CNS) holds immense significance. This technique provides unparalleled insights into the structure and function of this vital component of our nervous system.
The myelin sheath, composed of specialized cells known as Schwann cells in the PNS and oligodendrocytes in the CNS, acts as an insulating layer around nerve fibers. This insulation enables rapid and efficient transmission of electrical signals, facilitating communication throughout the nervous system.
Art-Labeling Activity for Myelin Sheath Analysis
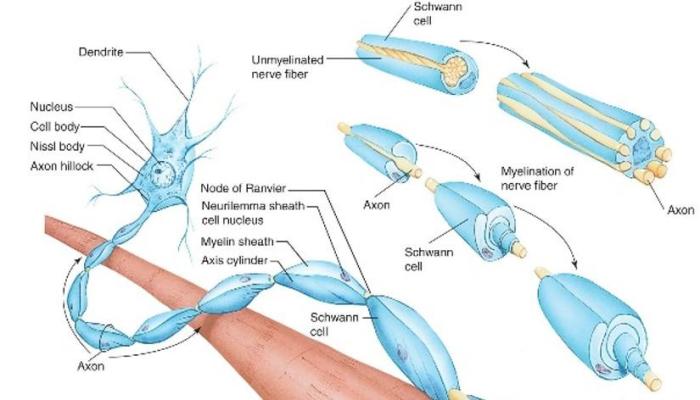
Art-labeling activity is a powerful tool in neuroscience research, enabling visualization and analysis of the myelin sheath, a critical component of the nervous system. This article explores the principles and applications of art-labeling techniques in studying the myelin sheath in the peripheral nervous system (PNS) and central nervous system (CNS).
Definition and Overview
Art-labeling activity involves labeling specific molecules or structures within a tissue sample using specialized markers or probes. In the context of myelin sheath analysis, art-labeling techniques are employed to visualize and study the myelin sheath, a lipid-rich insulating layer that surrounds axons in the nervous system.
The myelin sheath plays a crucial role in facilitating rapid and efficient transmission of electrical signals along nerve fibers.
Structural Differences between PNS and CNS Myelin Sheaths
The myelin sheath exhibits structural differences between the PNS and CNS. In the PNS, Schwann cells wrap around axons, forming a single myelin sheath segment. In contrast, in the CNS, oligodendrocytes extend multiple processes to wrap around several axons, forming multiple myelin sheath segments along each axon.
Art-Labeling Techniques for Myelin Sheath Analysis
- Immunohistochemistry: Uses antibodies to label specific proteins within the myelin sheath, allowing for visualization of myelin-associated proteins, such as myelin basic protein (MBP) or myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein (MOG).
- Electron Microscopy: Provides ultrastructural details of the myelin sheath, enabling visualization of its layered structure, thickness, and other morphological characteristics.
- Confocal Microscopy: Utilizes fluorescent probes to label specific components of the myelin sheath, allowing for three-dimensional visualization and analysis of its structure and organization.
Applications in Neuroscience Research
Art-labeling activity has significantly contributed to the study of myelin-related disorders. By labeling and analyzing the myelin sheath, researchers have gained insights into the pathogenesis of conditions such as:
- Multiple Sclerosis: Characterized by demyelination, the loss of myelin sheath, leading to impaired nerve function.
- Guillain-Barré Syndrome: An autoimmune disorder that attacks the myelin sheath in the PNS, causing muscle weakness and paralysis.
Limitations and Future Directions, Art-labeling activity the myelin sheath in the pns and cns
While art-labeling techniques provide valuable insights into the myelin sheath, they have limitations. Some techniques require tissue fixation, which can alter the myelin sheath structure. Additionally, the resolution and specificity of labeling can vary depending on the technique used.
Future research directions include developing non-invasive imaging techniques for myelin sheath analysis and exploring the use of advanced labeling methods, such as super-resolution microscopy, to obtain even more detailed information about the myelin sheath structure and function.
FAQ Summary: Art-labeling Activity The Myelin Sheath In The Pns And Cns
What is the purpose of the myelin sheath?
The myelin sheath insulates nerve fibers, enabling faster and more efficient transmission of electrical signals.
What are the differences between Schwann cells and oligodendrocytes?
Schwann cells are found in the PNS and wrap around individual nerve fibers, while oligodendrocytes are found in the CNS and can wrap around multiple nerve fibers.
How is the art-labeling activity used to study the myelin sheath?
Art-labeling techniques, such as immunohistochemistry and electron microscopy, are used to visualize and analyze the structure and function of the myelin sheath.