Process of reproducing shading in print is an intricate art form that requires a deep understanding of color theory, printing techniques, and design principles. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of reproducing shading effectively, providing invaluable insights for designers, printers, and anyone seeking to enhance their print materials with captivating visual depth.
From understanding the concept of shading and its importance in print reproduction to exploring various printing methods and troubleshooting common shading issues, this guide covers all aspects of the process. It equips readers with the knowledge and skills necessary to achieve optimal shading results, ensuring that their print designs stand out with exceptional visual appeal.
Process of Reproducing Shading in Print

Understanding Shading Techniques, Process of reproducing shading in print
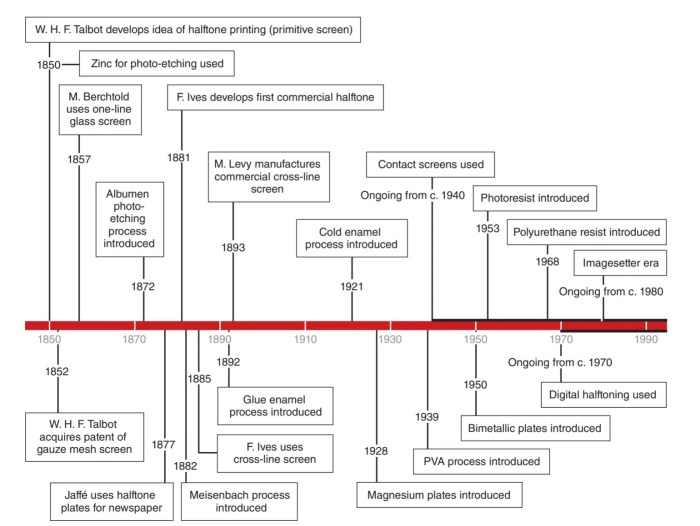
Shading, the technique of creating depth and dimension by varying the darkness of an area, is crucial in print reproduction. Common shading techniques include hatching, cross-hatching, and stippling.
Hatching involves creating parallel lines of varying thickness and spacing, while cross-hatching adds a second layer of lines perpendicular to the first. Stippling uses small dots to create shading.
Hatching and cross-hatching provide more control over the intensity and direction of shading, while stippling creates a softer, more diffused effect.
Color Reproduction in Shading
Color plays a vital role in shading. The color separation process involves dividing an image into its primary colors (cyan, magenta, yellow, and black), which are then printed separately.
Accurate color reproduction in shaded prints requires careful calibration of the printing press and proper ink selection. Tips include using a high-resolution image, adjusting color profiles, and calibrating the printer regularly.
Printing Methods for Shading
Offset printing excels in reproducing fine details and smooth transitions in shading. Digital printing offers convenience and flexibility but may have limitations in terms of color accuracy.
Screen printing is ideal for creating bold, vibrant shades and is commonly used for posters and textiles. The choice of printing method depends on the desired shading effect, budget, and turnaround time.
Optimizing Shading for Print
High image resolution ensures sharp shading reproduction. TIFF and PSD file formats preserve image quality during editing.
Common challenges include moiré patterns, banding, and color shifts. Moiré patterns can be minimized by using a higher screen frequency, while banding can be reduced by increasing the number of ink layers.
Design Considerations for Shading
Shading can enhance visual hierarchy, create depth, and convey emotions in print designs.
Effective shading involves balancing contrast, direction, and intensity. Examples include using light shades for highlights and dark shades for shadows to create a sense of depth.
Troubleshooting Shading Issues
Common shading problems include uneven shading, color misalignment, and fading.
Uneven shading can be caused by inconsistent ink flow or plate wear. Color misalignment can result from improper registration. Fading can be prevented by using UV-resistant inks and storing prints away from direct sunlight.
User Queries: Process Of Reproducing Shading In Print
What is the importance of shading in print reproduction?
Shading adds depth, dimension, and visual interest to print designs, enhancing their overall appeal and readability.
How does color separation impact shading reproduction?
Color separation breaks down an image into its individual color components, allowing for precise control over the reproduction of shading and color accuracy.
What are the advantages of using offset printing for shading?
Offset printing offers high-quality shading reproduction, sharp details, and a wide color gamut, making it ideal for reproducing complex shading effects.
How can I optimize images for printing to ensure optimal shading results?
Use high-resolution images, choose the appropriate file format, and calibrate your monitor to ensure accurate color representation.