In the context of intercultural competence critical scholars emphasize the – In the context of intercultural competence, critical scholars emphasize the multifaceted nature of cultural interactions, challenging traditional approaches that often overlook power dynamics, privilege, and intersectionality. This essay delves into the evolution, key concepts, and implications of critical intercultural competence, providing a comprehensive understanding of its significance in promoting social justice and fostering inclusive societies.
Critical intercultural competence acknowledges the complexities of cultural encounters, recognizing the influence of power structures and social inequalities. It encourages individuals to critically examine their own cultural biases and assumptions, fostering a deeper understanding of diverse perspectives and experiences.
Historical Context
The concept of intercultural competence has evolved significantly within critical scholarship. Initially, it was seen as a set of skills and knowledge that individuals could acquire to improve their interactions with people from different cultures. However, critical scholars have challenged this traditional approach, arguing that it often perpetuates cultural stereotypes and fails to address the power dynamics that shape intercultural interactions.
Key figures in the development of critical intercultural competence include Edward Said, Homi Bhabha, and bell hooks. Said’s work on Orientalism exposed the ways in which Western knowledge and power have shaped our understanding of non-Western cultures. Bhabha’s concept of hybridity challenged the idea of fixed cultural identities, arguing that individuals are constantly negotiating their identities in relation to multiple cultures.
Hooks’ work on intersectionality emphasized the importance of considering how different identities, such as race, gender, and class, intersect to shape intercultural experiences.
Critical Perspectives
Critical scholars have identified several limitations and biases in traditional approaches to intercultural competence. First, they argue that traditional approaches often focus on individual skills and knowledge, rather than addressing the systemic power dynamics that shape intercultural interactions. Second, they argue that traditional approaches often rely on essentialist notions of culture, which can lead to stereotypes and misunderstandings.
Third, they argue that traditional approaches often fail to take into account the experiences of marginalized groups, such as people of color, women, and LGBTQ people.
Key Concepts
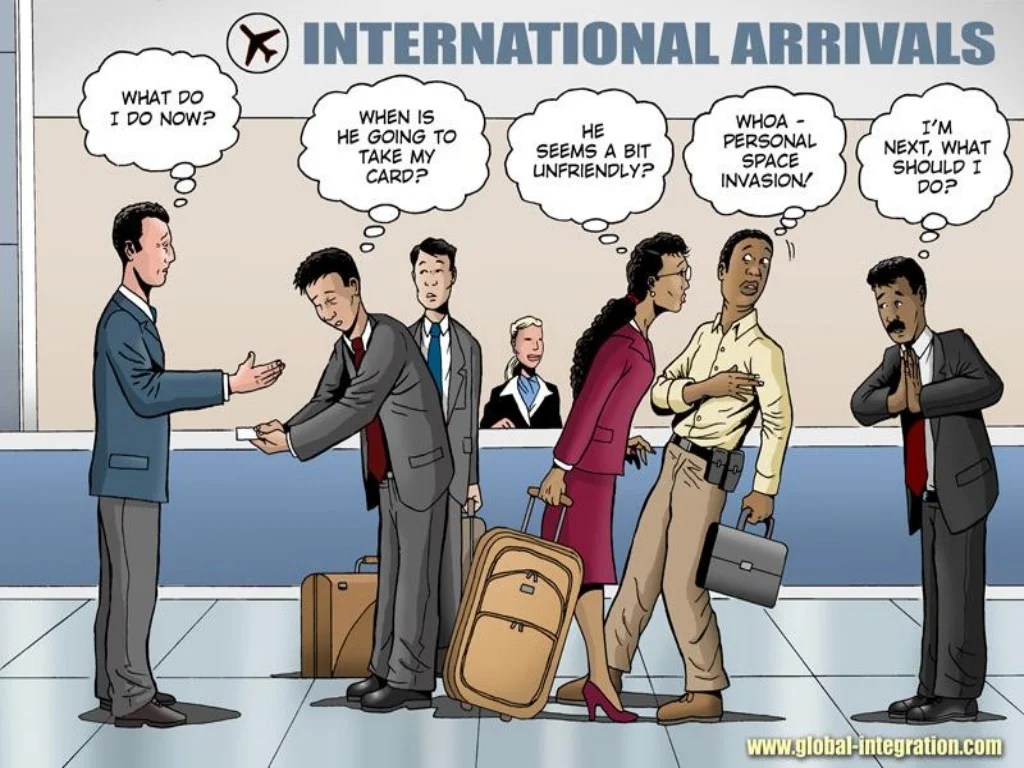

Critical scholars have developed a number of key concepts to help us understand intercultural competence. These concepts include:
- Cultural competence: The ability to understand and interact effectively with people from different cultures.
- Intercultural communication: The process of communicating across cultural boundaries.
- Critical consciousness: The ability to recognize and challenge the power dynamics that shape intercultural interactions.
- Cultural humility: The ability to approach intercultural interactions with an attitude of respect and openness.
Power and Privilege

Critical scholars have emphasized the role of power and privilege in intercultural interactions. They argue that power and privilege can shape the ways in which people from different cultures interact with each other. For example, people from dominant cultures often have more power and privilege than people from marginalized cultures, which can lead to misunderstandings and conflict.
Critical scholars have also challenged the traditional notion of cultural equality, arguing that it is often based on a false premise that all cultures are equal.
Intersectionality
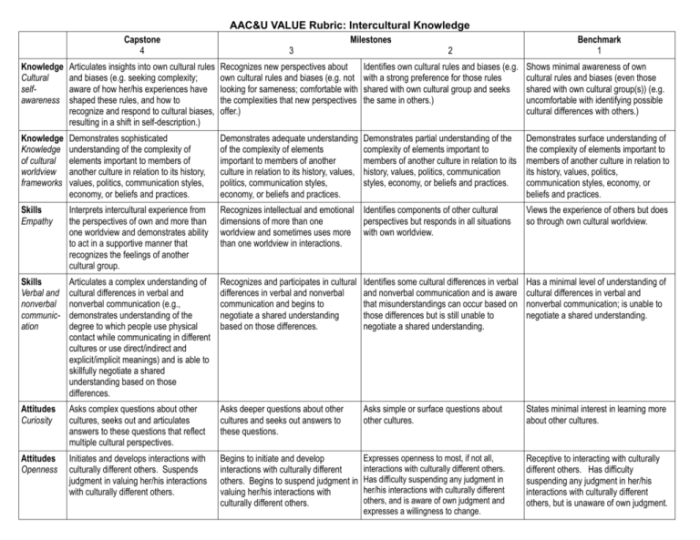
Critical scholars have also emphasized the importance of intersectionality in understanding intercultural competence. Intersectionality is the idea that different identities, such as race, gender, and class, intersect to shape our experiences of the world. This means that intercultural competence cannot be understood without taking into account the ways in which different identities intersect to shape intercultural interactions.
Social Justice: In The Context Of Intercultural Competence Critical Scholars Emphasize The
Critical scholars have argued that intercultural competence is essential for social justice. They argue that intercultural competence can help us to understand and challenge the power dynamics that shape intercultural interactions, and to create more just and equitable societies. Critical scholars have also used intercultural competence to promote social change, such as by developing educational programs and resources that help people to learn about different cultures and to develop intercultural skills.
Pedagogical Implications
The implications of critical intercultural competence for education are significant. Critical intercultural competence can help educators to create more inclusive and equitable classrooms, and to prepare students to live and work in a diverse world. There are a number of best practices for teaching intercultural competence in a critical way, including:
- Using critical pedagogy: Critical pedagogy is an approach to teaching that emphasizes the importance of social justice and critical thinking.
- Creating inclusive classrooms: Inclusive classrooms are classrooms that are welcoming and supportive of all students, regardless of their cultural background.
- Teaching about power and privilege: It is important to teach students about the role of power and privilege in intercultural interactions.
- Using experiential learning: Experiential learning is a type of learning that involves students in hands-on experiences.
User Queries
What is critical intercultural competence?
Critical intercultural competence is an approach to understanding and interacting with diverse cultures that acknowledges the role of power, privilege, and intersectionality in shaping cultural interactions.
Why is critical intercultural competence important?
Critical intercultural competence is important because it helps individuals to develop a deeper understanding of their own cultural biases and assumptions, and to critically examine the power dynamics and social inequalities that shape cultural interactions.
How can critical intercultural competence be used to promote social justice?
Critical intercultural competence can be used to promote social justice by fostering mutual respect, understanding, and collaboration among people from different cultural backgrounds, and by challenging traditional notions of cultural equality.