Embark on a journey into the realm of weathering, erosion, and deposition with our comprehensive weather erosion and deposition worksheet. This invaluable resource delves into the intricate processes that shape our planet’s landscapes, providing a captivating overview of these fundamental geological phenomena.
Through detailed explanations, engaging activities, and real-world examples, this worksheet empowers learners to unravel the complexities of Earth’s dynamic surface processes, fostering a deeper understanding of our planet’s ever-changing nature.
Weathering Processes
Weathering refers to the breakdown and alteration of rocks and minerals on Earth’s surface. It occurs due to exposure to various agents, including water, temperature changes, and biological activity. Weathering processes can be categorized into three main types:
- Physical weatheringinvolves the physical breakdown of rocks into smaller pieces without changing their chemical composition. Examples include frost wedging, exfoliation, and abrasion.
- Chemical weatheringinvolves the chemical alteration of rocks, resulting in the formation of new minerals. Examples include hydrolysis, oxidation, and carbonation.
- Biological weatheringinvolves the breakdown of rocks by living organisms, such as plants, animals, and microorganisms. Examples include root wedging, burrowing, and the release of organic acids.
The rate of weathering is influenced by several factors, including:
- Rock type: Different rock types have varying resistance to weathering.
- Climate: Temperature and precipitation patterns affect the intensity and type of weathering processes.
- Surface area: The larger the surface area of a rock, the more exposed it is to weathering agents.
- Time: Weathering processes occur over extended periods of time.
Erosion Processes
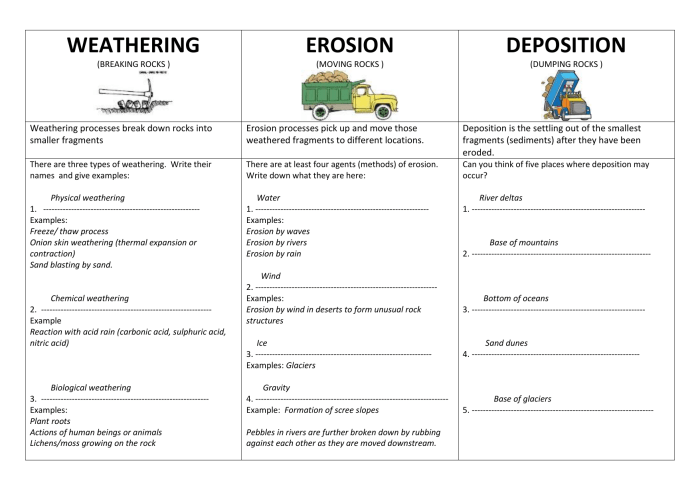
Erosion is the process by which weathered materials are transported away from their original location. It can occur through various mechanisms, including:
- Water erosionis caused by the movement of water, such as rainfall, runoff, and rivers. It can result in the formation of channels, gullies, and valleys.
- Wind erosionis caused by the movement of wind. It can transport fine particles, such as sand and dust, and can lead to the formation of dunes and loess deposits.
- Ice erosionis caused by the movement of glaciers and ice sheets. It can scrape and scour the land surface, creating features such as moraines and cirques.
Erosion is influenced by several factors, including:
- Type of erosion: Different erosion processes have varying effects on the landscape.
- Climate: Precipitation patterns and wind speed can affect the intensity of erosion.
- Vegetation: Vegetation can help stabilize the soil and reduce erosion.
- Soil structure: Soil texture and permeability influence the susceptibility to erosion.
Deposition Processes

Deposition is the process by which eroded materials are deposited in new locations. It occurs when the energy of the transporting agent decreases, causing the materials to settle out. Deposition can result in the formation of various landforms, such as:
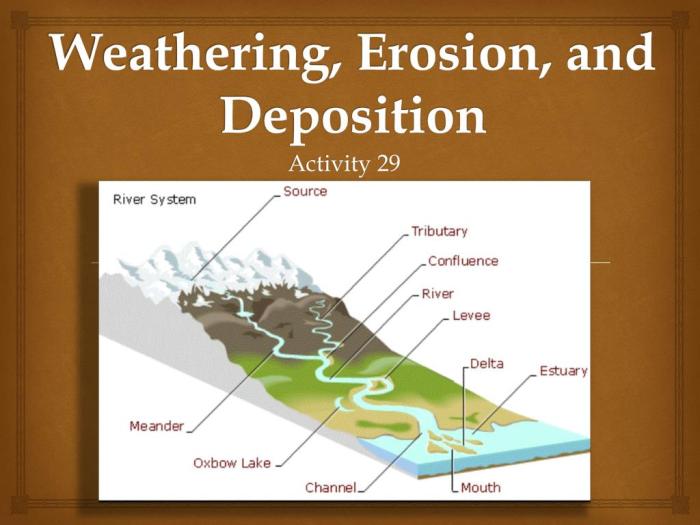
- Deltasare formed at the mouths of rivers where sediment is deposited as the river enters a larger body of water.
- Floodplainsare formed along riverbanks where sediment is deposited during flooding.
- Sand dunesare formed by the accumulation of wind-blown sand.
Deposition is influenced by several factors, including:
- Type of depositional environment: Different depositional environments have unique characteristics that influence the type of landforms formed.
- Sediment supply: The availability of sediment for deposition is crucial.
- Energy of the transporting agent: The energy of the agent (e.g., water, wind) determines the size and distance of sediment transport.
- Climate: Climate conditions can affect the availability of sediment and the energy of the transporting agent.
Answers to Common Questions: Weather Erosion And Deposition Worksheet
What is the difference between weathering and erosion?
Weathering refers to the breakdown of rocks and minerals at their source, while erosion involves the transportation of weathered materials away from their original location.
How does vegetation help prevent erosion?
Vegetation acts as a protective barrier, intercepting rainfall and reducing the impact of wind, thereby minimizing soil erosion.
What are the different types of depositional environments?
Common depositional environments include deltas, floodplains, sand dunes, and glacial moraines.
