Lithium sulfate and lead ii acetate – Lithium sulfate and lead(II) acetate, two inorganic compounds with distinct properties and applications, provide a captivating subject for scientific exploration. This discourse delves into their chemical formulas, solubility, physical characteristics, reactivity, industrial uses, and safety considerations, unveiling the intricacies of these intriguing substances.
With their unique chemical compositions and diverse applications, lithium sulfate and lead(II) acetate present a fascinating study in the realm of inorganic chemistry.
Chemical Properties
Lithium sulfate is a colorless, crystalline solid with the chemical formula Li 2SO 4. It is highly soluble in water, forming a neutral solution. Lead (II) acetate, on the other hand, is a white, crystalline solid with the chemical formula Pb(CH 3COO) 2. It is also soluble in water, but its solubility is lower than that of lithium sulfate.
Physical Properties
Lithium sulfate has a melting point of 860 °C (1580 °F), while lead (II) acetate has a melting point of 280 °C (536 °F).
Chemical Reactions
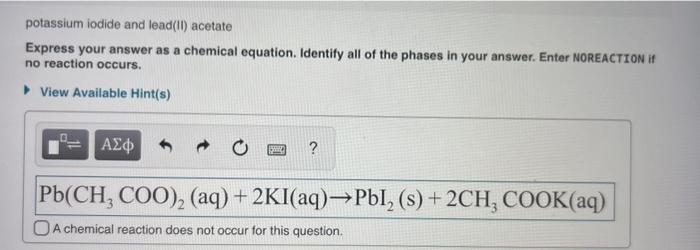
Lithium sulfate is a relatively unreactive compound. It does not react with most acids or bases. Lead (II) acetate, on the other hand, is more reactive. It reacts with acids to form lead (II) salts and acetic acid. It also reacts with bases to form lead (II) hydroxide and acetic acid.
Industrial Applications

Lithium sulfate is used in a variety of industrial applications, including:
- As a flux in the production of glass and ceramics
- As a mordant in the dyeing of textiles
- As an electrolyte in lithium-ion batteries
Lead (II) acetate is also used in a variety of industrial applications, including:
- As a mordant in the dyeing of textiles
- As a preservative in wood
- As a catalyst in the production of other chemicals
Safety Considerations: Lithium Sulfate And Lead Ii Acetate
Lithium sulfate is a relatively safe compound, but it can cause skin irritation. Lead (II) acetate is a more toxic compound, and it can cause a variety of health problems, including:
- Skin irritation
- Eye irritation
- Respiratory problems
- Lead poisoning
Q&A
What are the industrial applications of lithium sulfate?
Lithium sulfate finds use in the production of glass and ceramics, as a flux in soldering and welding, and as a component in electrolytes for lithium-ion batteries.
What safety precautions should be taken when handling lead(II) acetate?
Lead(II) acetate is toxic and should be handled with care. Proper ventilation, protective clothing, and gloves are essential to minimize exposure. Avoid contact with skin and eyes, and wash hands thoroughly after handling.